ANSWER KEY
CHEMISTRY: CHAPTER 4
SOLUTIONS
| 1. |
CL- ions come from both sources |
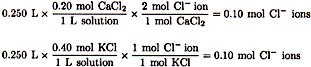
| Mixing together in 0.50 liter of solution |
![]()
| Other answers are results when the values provided are used incorrectly. |
| The correct choice is (D). |
| 2. |
Using the quantity of H2SO4 provided gives |
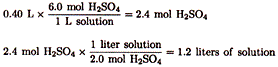
| Since the final volume will be 1.2 liters and water is to be added to 0.40 liters of more concentrated H2SO4, the volume of water needed is 0.80 liters, the difference between 1.2 liters and 0.40 liters. (Note: in a proper laboratory procedure, acid would be added to water.) |
| The correct choice is (C). |
| 3. |
The highest freezing point will be found in the solution that has the lowest concentration of dissolved particles, that is, the solution closest to "pure" water. Since all solutions have the same concentration, the extent of ionization or dissociation contributes to the quantity of particles in solution. Both ammonium chloride, NH4Cl, and ammonium hydrogen sulfate, NH4HSO4, dissociate to form two moles of ions per mole of compound. Nitrogen pentoxide, N2O5, dissolves in water to form two moles of nitric acid, HNO3, hence four moles of ions per mole of compound. Ammonium phosphate, (NH4)3PO4, dissolves and dissociates to form four moles of ions (three NH4+ and one PO43-) per mole of comound. Urea, (NH2)2CO, is soluble but does not dissociate or ionize. Thus, the urea solution has the lowest concentration of dissolved particles. |
| The correct choice is (A). |
| 4. |
Density is defined as mass per unit volume. When molality is known, moles of solute per kilogram of solution can be calculated. |
![]()
| To obtain mol solute per kilogram of solution, add mass of solute present to 1.00 kg solvent as shown above. |
![]()
| The denominator gives the mass of the solute + solvent (the solution). In order to calculate density, a connection to volume of solution must be known. Such a connecction is molarity, moles of solute per liter of solution. The expression below shows how to use the known information to obtain density. |
![]()
| The correct choice is (B). |
| 5. |
Mole fraction is defined as the ratio of moles of solute to the sum of the moles of all components in the mixture. Thus, the mole fraction of sulfuric acid dissolved in water is given by |
![]()
| For the given solution, |
![]()
| rearranged to form simple fraction |
![]()
| The correct choice is (B). |
| 6. |
Solubility is a statement of the quantity (usually mass or moles) of solute that can be dissolved in a given quantity (usually mass or volume) of a given solvent at a specified (or generally agreed-upon) temperature to form a saturated solution. It is an intensive physical property of the solute/solvent pair. Increasing surface area and volume of solvent may affect the rate at which the dissolving process occurs but does not affect solubility. Increasing pressure increases the solubility of a gas in a liquid solvent but does not affect the solubility of solids appreciably. Increasing the mass of solute available does not affect the capacity of the solvent to dissolve that solute. Increasing the temperature changes the solubility of ionic solutes, most often increasing that solubility. |
| The correct choice is (C). |
| 7. |
A standard solution is prepared by mixing a specified quantity of solute into sufficient solvent to produce a specified quantity of solution. Most often this is a specified mass of solute in a specified volume of solution. The crucible is used to contain the hydrated salt as it is dried over a flame. A laboratory balance is used to weigh the dried solute. A funnel is used to facilitate transfer of water into the volumetric flask. There is no essential role for the thermometer. |
| The correct choice is (C). |
| 8. |
Percent methanol by mass calls for mass methanol in the numerator and mass of solution (solute + solvent) in the denominator. |
![]()
| The correct choice is (C). |
| 9. |
If the final rinsing of a buret in a titration experiment is taken with water rather than the standard solution, the standard solution becomes slightly diluted by residual water in the buret as its initial volume reading is taken. Thus, an apparently slightly larger quantity of the standard solution will have been added to the reaction mixture when the endpoint is reached. This causes the number of moles of base used to be reported too large and therefore the number of moles of acid reacting is also reported too large. The mistake does not affect the volume of solute used for the solid acid. (That volume is not used in any calculation for the assigned result.) Only statement III is correct. |
| The correct choice is (C). |
| 10. |
A substance whose water solution is both saturated and dilute is a substance that is not very soluble. Such a substancs is silver acetate, a salt of a heavy metal. All the other substances are very soluble in water. |
| The correct choice is (B). |
| 11. |
The substance least likely to be found in a concentrated solution is a substance that is not very soluble in water. Of the substances listed, magnesium hydroxide, a Group 2 hydroxide, is least soluble. |
| The correct choice is (C). |
| 12. |
Parts per million refers to mass of solute per million units of solvent. Drinking water with 0.050 ppm arsenic contains 0.050 g arsenic per 106 (million) grams of water. One way to respond to this question is to change each answer to the same units as given, i.e., ..?.. g arsenic per 106 (million) grams of water. |

| The value, 0.050 mg As per liter of water, is another way to express 0.050 ppm. |
| The correct choice is (B). |
| 13. |
At 35ºC, a saturated solution contains between 35 and 40 grams of solute per 100 grams of water. That is approximately 0.5 mol/0.1 kg solvent which is 5 M (molal). |
| The correct choice is (E). |
| 14. |
At 75ºC, a saturated solution of KCl contains about 50 g KCl per 100 g water, producing a solution with total mass of 150 g. Thus the percent by mass of KCl is about 1/3 or 33%. |
| The correct choice is (A). |
| 15. |
Since no further changes are occuring and the mixture is below the saturation point (45 g KCl per 100 g water), the system must be an unsaturated solution. |
| The correct choice is (D). |
| 16. |
Since a white crystalline solid forms during the cooling process, one can conclude that the solution has become saturated. At the final temperature of 35ºC, the 100 grams of solute (H2O) can dissolve about 35 grams of this solute (KCl), producing 135 grams of solution. Note that choice (C) specifies 100 grams of solution which is not correct. |
| The correct choice is (E). |
| 17. |
Since the mole fraction of toluene in this solution is only 0.40 (less than 0.5), the vapor pressure of the solution will be closer to the value of the vapor pressure for benzene whose mole fraction is 0.60. A 0.50 mole fraction solution would have a vapor pressure slightly less than 50 mmHg. At Xbenzene = 0.60, the vapor pressure is somewhat greater than 50, choice (D), but not as high as choice (E). |
| The correct choice is (D). |
| 18. |
The mole fraction provided in question 17 gives the ratio of molecules in the liquid phase. The vapor phase over a solution containing two volatile liquids is enriched in the more volatile of the two components. Since benzene is more volatile than toluene, the vapor phase will have a greater ratio of benzene molecules to toluene molecules than the liquid. |
| The correct choice is (B). |
| 19. |
The Tyndall effect is the glow observed along the path of a beam of light shining though a colloid. It is caused by the scattering of light as photons strike the dispersed particles of a colloid. This effect is not observed in a solution because the dispersed particles are too small to affect light. Since the particles of a suspension are much larger, that type of dispersion is opaque to visible light. |
| The correct choice is (A). |
| 20. |
The stearate ion, C17H35COO-, is large enough to have a charged part that is attracted to water and an uncharged part that is attracted to nonpolar molecules. Hydrophobic molecules are likely to be nonpolar molecules that form strong intermolecular attractions with each other and thus "repel" water. In the presence of the stearate ion, such repulsion decreases. This accounts for the cleaning action of ordinary soap. |
| The correct choice is (B). |
| 21. |
Adding water to a solution of potassium nitrate will cause the solution to become more dilute in potassium nitrate. In addition, its volume will increase. At lower concentration, the solution will have higher vapor pressure and higher freezing point. Its mass per unit volume (density) will decrease. Its properties become more like pure water. |
| The correct choice is (E). |
| 22. |
In this solution, the addition of NaCl to water causes density to increase, vapor pressure to decrease, freezing point to decrease, and osmotic pressure to increase. The lower vapor pressure accounts for the increase in the boiling point as the solute is added to the solution. |
| The correct choice is (C). |
| 23. |
In a spontaneous,
exothermic dissolving process, |
| The correct choice is (C). |
| 24. |
Increasing the temperature while maintaining contact with excess solute causes more solute to dissolve. Both molality and density of the solution increase. The solution remains saturated because it remains in contact with excess solute. |
| The correct choice is (E). |
| 25. |
Increasing the temperature of any aqueous NaCl solution causes the vapor pressure to increase because the vapor pressure of the solvent increases. The number of ion pairs in solution remains the same because a dilute solution of an ionic solid such as NaCl is fully dissociated. The difference between the boiling point and the freezing point remains the same because the concentration of the solution remains the same. |
| The correct choice is (A). |