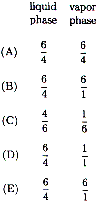CHEMISTRY:
CHAPTER 4
SOLUTIONS
| 1. |
What is the final concentration of Cl-
ion when 250 mL of 0.20 M CaCl2 solution is
mixed with 250 mL of 0.40 M KCl solution? (Assume
additive volumes.) |
 |
(A) |
0.10 M |
| (B) |
0.20 M |
| (C) |
0.30 M |
| (D) |
0.40 M |
| (E) |
0.60 M |
| 2. |
What volume of water should be added
to 0.40 L of 6.0 M H2SO4 solution
to produce a solution that is 2.0 M H2SO4?
|
 |
(A) |
0.40 L |
| (B) |
0.80 L |
| (C) |
1.2 L |
| (D) |
1.6 L |
| (E) |
2.4 L |
| 3. |
Which of the following 0.20 M water
solutions has the highest freezing point? (Assume ideal
behavior.) |
 |
(A) |
urea, (NH2)2CO |
| (B) |
nitrogen pentoxide, N2O5
|
| (C) |
ammonium chloride, NH4Cl |
| (D) |
ammonium phosphate, (NH4)3PO4
|
| (E) |
ammonium hydrogen sulfate, NH4HSO4
|
| 4. |
A water solution of sucrose (C12H22O11,
molar mass = 342) is known to be 6.0 molal. What one
additional characteristic of the solution could be used
to determine its density? |
 |
(A) |
mass |
| (B) |
molarity |
| (C) |
boiling point |
| (D) |
freezing point |
| (E) |
percent by mass |
Solutions
| 5. |
Which expression gives the mole
fraction of H2SO4 in a water
solution that contains 3.0 moles of H2SO4
in 90. grams of water? |
| 6. |
Which change is most likely to
increase the solubility of an ionic solid in water? |
 |
(A) |
increasing the surface area of the
solid in the system |
| (B) |
increasing the volume of water
available in the system |
| (C) |
increasing the temperature of the
system |
| (D) |
increasing the external pressure on
the system |
| (E) |
increasing the mass of ionic solid
available in the system |
| 7. |
What piece of laboratory apparatus is
least likely to be used to prepare a quantity of standard
1.00 M BaCl2 using solid BaCl2.2H2O
and distilled water? |
 |
(A) |
funnel |
| (B) |
crucible |
| (C) |
thermometer |
| (D) |
volumetric flask |
| (E) |
laboratory balance |
| 8. |
What is the percent methanol by mass
in a solution that contains 20 grams of methanol,
CH3OH, in 30 grams of water? |
 |
(A) |
20% |
| (B) |
33% |
| (C) |
40% |
| (D) |
60% |
| (E) |
67% |
Solutions
| 9. |
A standard solution of sodium
hydroxide can be used in a titration experiment to
determine the formula mass of a solid acid. A common
mistake in such a titration experiment is the failure to
rinse the buret with the standard solution after the
final water rinse but before measurements of the volume
of the standard solution are taken. This mistake accounts
for which of the following results? |
 |
I. |
|
The volume of the standard solution
used in the titration reaction is reported too small. |
| II. |
The volume of the solute used to
dissolve the unknown acid is reported too small. |
| III. |
The number of moles of unknown acid
used in the titration reaction is reported too large. |
 |
(A) |
I only |
| (B) |
II and III only |
| (C) |
III only |
| (D) |
I and III only |
| (E) |
I, II, and III |
| 10. |
Which substance is most likely to be
found in an aqueous solution that is both saturated and
dilute at room temperature? |
 |
(A) |
sucrose |
| (B) |
silver acetate |
| (C) |
sodium chloride |
| (D) |
ammonium carbonate |
| (E) |
potassium hydroxide |
| 11. |
Which substance is least likely to be
found in an aqueous solution that is concentrated? |
 |
(A) |
sodium phosphate |
| (B) |
hydrogen bromide |
| (C) |
magnesium hydroxide |
| (D) |
aluminum chloride |
| (E) |
ammonium nitrate |
| 12. |
The level of arsenic permitted in
drinking water is 0.050 ppm (parts per million). Which of
the following is another way to express that same
concentration? |
 |
(A) |
0.050 mg As/milliliter H2O |
| (B) |
0.050 mg As/liter H2O |
| (C) |
0.050 g As/million liters H2O
|
| (D) |
0.050 mg As/million liters H2O
|
| (E) |
0.050 mg As/million grams H2O
|
Solutions
Questions 13-14 refer to the solubility curve
for KCl in water as shown below.
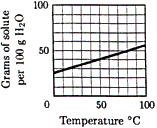
| 13. |
What is the molality of a saturated
solution of KCl (molar mass 74.6) at 35ºC? |
 |
(A) |
0.37 |
| (B) |
0.50 |
| (C) |
2.0 |
| (D) |
3.7 |
| (E) |
5.0 |
| 14. |
A saturated solution of KCl at 75ºC
contains 100 g water. Which value is closest to the
percent by mass of KCl in the solution? |
 |
(A) |
33 |
| (B) |
50 |
| (C) |
60 |
| (D) |
67 |
| (E) |
75 |
Questions 15 and 16 refer to the solubility
curve for KCl in water shown above. A mixture containing 100 g H2O
and 40. g KCl is warmed to 60ºC and thoroughly stirred until no
further changes occur.
| 15. |
The resulting system is best desribed
as |
 |
(A) |
a colloid |
| (B) |
a suspension |
| (C) |
a saturated solution |
| (D) |
an unsaturated solution |
| (E) |
an isotonic solution |
| 16. |
When the system is cooled from 60ºC
to 30ºC, a white crystalline solid forms. Which is the
best description of the liquid phase of the system? |
 |
(A) |
50 g solution including 20 g solute |
| (B) |
60 g solution including 40 g solute |
| (C) |
100 g solution including 35 g solute |
| (D) |
120 g solution including 20 g solute |
| (E) |
135 g solution including 35 g solute |
Solutions
Questions 17 and 18 refer to the table
of information below. The molar masses and vapor pressures of
benzene and toluene at 20ºC are given in this table.

| 17. |
Consider a solution whose mole
fraction is 0.40 toluene Xtoluene = 0.40. Which location on this scale is the
best estimate of the vapor pressure of the solution? |
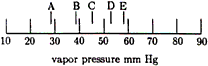
 |
(A) |
A |
| (B) |
B |
| (C) |
C |
| (D) |
D |
| (E) |
E |
| 18. |
For the solution described in question
17, which gives the best comparison between the ratio of
the number of molecules of each substance in the liquid
phase and the ratio of the number of molecules of each
substance in the vapor phase over the liquid at 20ºC? |
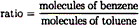
Solutions
| 19. |
Which accounts for the Tyndall effect
in colloids? |
 |
(A) |
scattering of light by particles of
matter |
| (B) |
absorption of light by particles of
matter |
| (C) |
absorption of light of specific
wavelength in the visible range |
| (D) |
absorption of light of specific
wavelength in the ultraviolet range |
| (E) |
alternating patterns of refraction and
reflection of light by lattice particles |
| 20. |
A hydrophobic colloid is most likely
to be stabilized in water by the presence of |
 |
(A) |
sodium ions |
| (B) |
stearate ions |
| (C) |
hydrogen ions |
| (D) |
sucrose molecules |
| (E) |
benzene molecules |
| 21. |
Which applies to a 1.0 molar solution
of potassium nitrate in water? |
 |
I. |
|
Adding water raises the freezing
point. |
| II. |
Adding water increases the vapor
pressure of the solution. |
| III. |
Adding water decreases the density of
the solution. |
 |
(A) |
I only |
| (B) |
II and III only |
| (C) |
I and III only |
| (D) |
II and III only |
| (E) |
I, II, and III |
| 22. |
Compared to water, a 0.20 M solution
of NaCl will have all of the following properties EXCEPT:
|
 |
(A) |
greater density |
| (B) |
lower vapor pressure |
| (C) |
lower boiling point |
| (D) |
lower freezing point |
| (E) |
greater osmotic pressure |
Solutions
| 23. |
In a spontaneous, exothermic
dissolving process, which of these values has a negative
sign? |
 |
I. |
|
 Gsoln Gsoln |
| II. |
 Hsoln Hsoln |
| III. |
 T T |
 |
(A) |
I only |
| (B) |
III only |
| (C) |
I and II only |
| (D) |
II and III only |
| (E) |
I, II, and III |
| 24. |
A saturated solution of KNO3
in equilibrium with excess solute is prepared at 20ºC.
Which of the following describe the solution after the
temperature of the system is increased to 40ºC while
still in contact with excess solute? |
 |
I. |
|
The molality of the solution
increases. |
| II. |
The solution remains saturated. |
| III. |
The density of the solution increases.
|
 |
(A) |
II only |
| (B) |
III only |
| (C) |
I and III only |
| (D) |
II and III only |
| (E) |
I, II, and III |
| 25. |
A dilute solution of NaCl is prepared
at 20ºC. Which of the following describes the solution
after the temperature of the solution is increased 40ºC?
|
 |
I. |
|
The vapor pressure of the solution
increases. |
| II. |
The number of ion pairs in solution
increases. |
| III. |
The difference between the freezing
point and the boiling point increases. |
 |
(A) |
I only |
| (B) |
III only |
| (C) |
I and II only |
| (D) |
I and III only |
| (E) |
I, II, and III |
[Answer
Key]
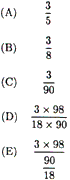


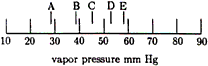
![]()